5 mai 2020
Recovering from Ransomware Attacks: The Magic of an Immutable Backup Architecture
Find out why backups are one of the most if not the most important defences against ransomware, and how Rubrik offers a backup solution that can help.

Ransomware has been ahot topic in cybersecurity for years, with many stories of organizations thatcan no longer access their business-critical data after the attackers haveencrypted access to production files and storage devices. While cybersecurityteams have invested in a myriad of protection tools, extortionists continue tofind new mechanisms to encrypt organizations' data.
Backups are one of themost if not the most important defences against ransomware. But advancedransomware is now targeting backups modifying or completely wiping them out eliminating that last line of defence and driving large ransom payouts.
Rubrik's uniquelyimmutable filesystem natively prevents unauthorized access or deletion ofbackups, allowing IT teams to quickly restore to the most recent clean statewith minimal business disruption. This blog walks you through their immutablearchitecture and robust security controls that can harden your data againstcyberattacks.
TheEffects of Ransomware
Ransomware is designedto encrypt your data so that it is no longer usable. Often, this meansencryption of data held on primary storage to overwhelm IT and requires massiverecovery efforts from tape or other archives. Additionally, lower levelencryption of the Master Boot Record (MBR) or other operating system levelencryption is used to prevent booting and other common operations. Forvirtualized environments, the shared data storage used to host virtual machinesis a primary target, such as with NFS-backed datastores. This can effectivelybring down critical services in an organization. The attackers would thendemand a ransom to unlock the data so that services can be resumed.
HowRubrik Has Helped Customers
Several Rubrikcustomers have successfully survived a ransomware attack through the use of theirimmutable solution and instant recoveries as part of a defence in depthstrategy.
For example, the City of Durham in North Carolina detected aransomware attack on Friday, March 6, and its leaders credited their quickresponse to Rubrik's backup solution. Durham Mayor Steve Schewell said, Thecity can be assured that our backups are very good because they're immutable.[This means that] they could not be consumed by ransomware.
As a result, they wereable to quickly restore critical city services, including access to 911. Inaddition, Kerry Goode, Durham CIO, emphasized that core business systems,including ones that manage payroll, were back online by the start of thebusiness week.
Kern Medical Center discovered a large ransomware attackin June 2019 when users reported they couldn't access their systems. They wereable to recover 100% of the impacted systems protected by Rubrik withinminutes, including recovering their business-critical electronic medical recordsystem. CTO Craig Witmer said, After the incident, we were so impressed thatwe moved more of our legacy systems to Rubrik and are fully confident thatRubrik's immutable backups will protect us from future incidents.
How DoYou Recover from a Ransomware Attack?
Data backups can be aneffective way to restore data that has been locked/encrypted by the attack.However, what if your backup data isalso encrypted or deleted bya ransomware attack? How do you ensure that your backup data is not vulnerableto these attacks?
The KeyIs Immutable Backups
While primary storagesystems need to be open and available for client systems, your backup datashould be immutable. This means that once data has been written it cannot beread, modified or deleted by clients on your network. Immutability can help toensure recovery when production systems are compromised.
This goes well beyondsimple file permissions, folder ACLs or storage protocols. The concept ofimmutability needs to be baked into the backup architecture so that no securityexposure can tamper with the backups.
How RubrikIs Designed for Immutability
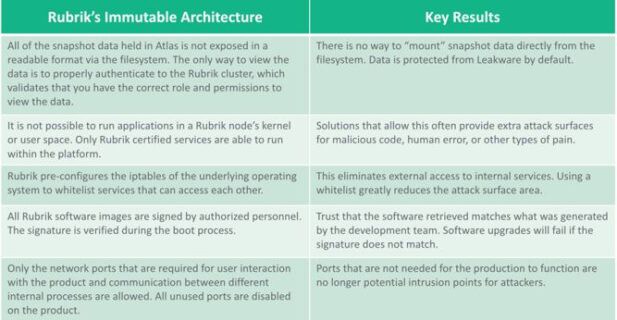
Rubrik uses animmutable architecture by combining an immutable filesystem with a zero trust cluster design inwhich operations can only be performed through authenticated APIs.
Rubrik's approach isin contrast with general purpose storage that uses standard protocols such asNFS or SMB to advertise their availability to a wide assortment of clients. Datamanagement solutions using general purpose storage can potentially have limitedor ineffective means for securely transacting data and, in some cases, leavefiles in their native format while allowing clients to read the backup datadirectly. This puts an extra burden on the customer to secure the storageindependent of their data management solution.
AnImmutable Distributed Filesystem
Rubrik constructedAtlas, an immutable Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) that was largelyPOSIX-compliant. This provides tight controls over which applications canexchange information, how each data exchange is transacted and how data isarranged across physical and logical devices. Atlas is custom designed to be adistributed and immutable file system for writing and reading data for otherRubrik services.
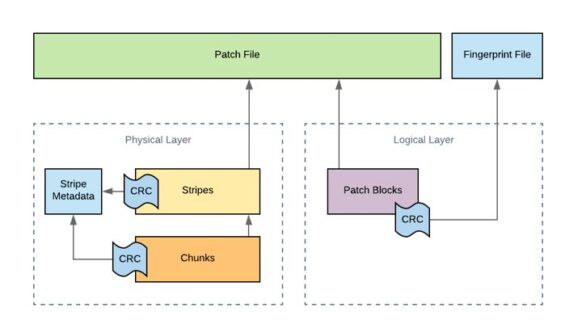
Immutability is provided across two layers: the logical layer (Patch Files, Patch Blocks) and the physical layer (Stripes, Chunks). The dynamics between these two layers will be explained further in the next few sections.
The Logical Layer
All customer data brought into the system is written into a proprietary sparse file called a Patch File. These are append-only files (AOFs), meaning that your data can only be added to the Patch File while it is marked as being open. All of the customer snapshot and journal data is held within Atlas, which enforces the use of Patch Files in the underlying directory structure. This powerful filesystem will refuse writes at the API level that are not append-only, such as situations in which the write offset value does not equal the file size.
Atlas has totalcontrol over how and where customer data is written.
If your backup data has been modified, then it's essentially worthless. Rubrik solved for this by ensuring that checksums are generated for each Patch Block within a Patch File. These checksums are computed and written to a Fingerprint File stored alongside the Patch File. Rubrik always does a fingerprint check before committing any data transformations. This ensures that the original file remains intact with forced validation during read operations.
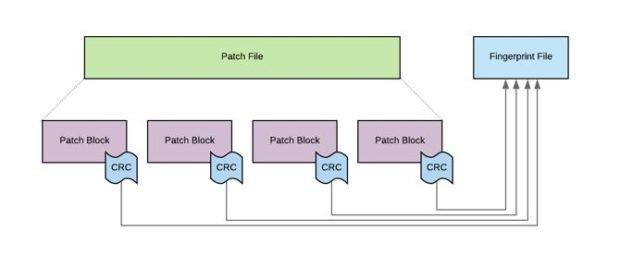
In order to counter a ransomware attack, the original, validated data must be restored from backup. Rubrik routinely verifies the Patch Blocks against their checksums to ensure data integrity at the logical Patch Block level. Patch Files are not exposed to any external systems or customer administrator accounts. This ensures that meticulous care is taken to restore exactly what you originally stored in a backup.
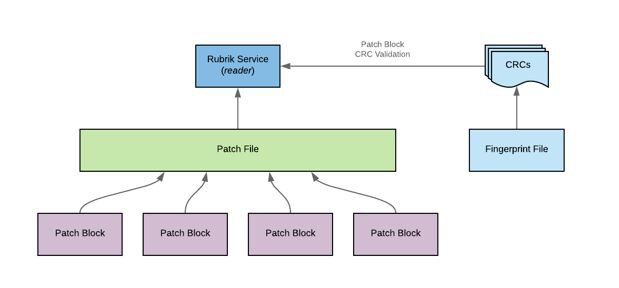
In a traditional approach, administrative access is granted to the filesystem especially when using general purpose storage which presents further confidentiality and integrity challenges and gives Leakware another attack vector. In addition, many traditional solutions simply restore whatever data is located in the backup folder or volume without performing validation and other due diligence on the data
The Physical Layer
While the logical layer focused on data integrity at the file level, the physical layer is focused on writing customer data across the immutable cluster to achieve data integrity and data resiliency. To do this, Patch Files are logically divided into fixed length segments called Stripes. As Stripes are written, the AOF computes a Stripe level checksum, which it stores within each Stripe Metadata.
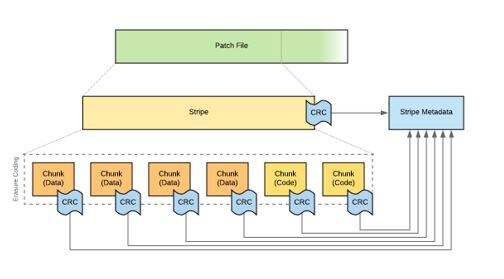
Stripes are furtherdivided into physical Chunks stored on physical disks held within the Rubrikcluster. Activities such as replication and erasure coding occur at the Chunklevel. Just as with Patch Files, as each Chunk is written, a Chunk checksum iscomputed and stored in the Stripe Metadata alongside the list of chunks. Thesechecksums are periodically recomputed as part of Atlas' background scan byreading the physical Chunks and comparing against the checksums in the StripeMetadata. Additionally, if a data rebuild is needed, the resiliency provided byerasure coding is automatically leveraged in the background.
ZeroTrust Cluster Design
Traditional approachesto cluster security often rely on a full trust model in which all members ofthe cluster are able to communicate with one another. In some cases, thisincludes root level authority, no mutual authentication checks and the abilityto read or modify customer data that is held within the filesystem. Thiscreates a weak surface area when designing a defence in depth architecture; ifbackup data can be compromised, there is no path to restoration when disruptionoccurs.
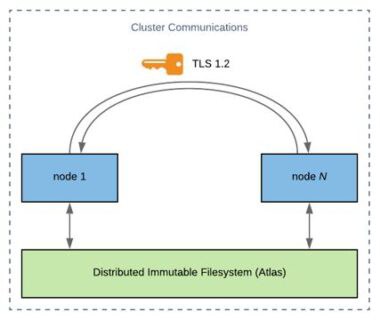
Secured Cluster Communications
Each cluster has some number of nodes that need to communicate with one another. This means there is a need to validate each node that wants to exchange data. At Rubrik, all of their intra-node and inter-cluster communication, as well as communication with external applications, use the TLS protocol with certificate-based mutual authentication for secure communication.
Rubrik does not use insecure protocols, such as NFS or SMB, to relay information within the cluster; all communication is performed through secure and trusted channels. In fact, all their internal communications use TLS 1,2 with strong cipher suites and Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS).
Each Rubrik clustershipped to a customer uses strong, randomized passwords on a per-node basis.There is no concept of a admin/admin style of default local authenticationthat is easily searchable on the web to add an attack vector.
Systems Hardening Standards
There are numerous other elements in position to protect the integrity of the system through internal hardening standards. Here are a few that help combat ransomware:
AuthenticatedAPIs
Rubrik adopted anAPI-first design as part of the architecture. They require authentication toall endpoints that are used to operate the solution. Authentication can behandled via credentials or secure token. This includes environments using theirRole-Based Access Control (RBAC) or Multi-tenancy features to logically dividethe roles, features and resources that are under management. Rubrik's CLI, SDKsand other tools consume the API and are held to the same security requirements.
API endpoints thatcontrol the underlying behaviour of the system require an additional level ofauthorization that can only be supplied from a certified technical supportengineer. This prevents a malicious actor from being able to alter the behaviourof a Rubrik cluster.
Conclusion
Numerous resources onthe Internet advocate for a Defence in Depthstrategy. This combinesefforts across employee education and enablement, rapid deployment of patchesand a solid backup and recovery plan.
This post describedhow Rubrik uses a combination of data immutability and a zero trust clusterdesign to build a great product for protecting and recovering data. Rubrik helpsorganizations further strengthen their ransomware response strategy with anapplication called Radar to increase visibility into the scope of attack. Thisallows organizations to quickly pinpoint which applications and files wereimpacted and where they reside to further minimize business impact. Learn more about Radar.
Many customers need tobe able to reliably recover from ransomware attacks to ensure minimal downtimeof their critical services. A product with a truly immutable architectureprovides customers the peace of mind that, when they need to, they can alwaysaccess the data to recover from such attacks.
To learn more, schedule an in-person or virtual meeting with CDW and Rubrik today.
